If you use open source projects from GitHub or GitLab in your infrastructure, you have probably established workflows to create project builds that you can install. You might create builds regularly and execute them in a similar manner across projects. Let's say you want to build the code changes in Fedora Linux or CentOS Stream for each commit, release, or pull request in these projects. Packit can automate this policy, fold into a CI/CD pipeline, and do even more.
Packit is an open source project that tests and builds RPM packages on Fedora Linux, CentOS Stream, and other distributions to ease the integration of upstream projects with the distributions.
This article focuses on Packit Service, which operates on GitHub and GitLab. You can also install a command line interface (CLI) locally to run Packit on your desktop or laptop.
Setting up Packit in 3 steps
Setting up Packit is pretty straightforward. Follow these three steps:
- Create a valid Fedora Account System account (if you don't already have one).
- Install our GitHub application on GitHub Marketplace, or configure a webhook on GitLab (depending on where your project lives).
- Provide your FAS username, which will be verified (on Github, the verification is automatic).
That's all! Now you can add a configuration file to your project's repository and start setting up Packit service jobs.
Most jobs require an RPM spec file. You can either place the spec file directly in your upstream repository or tell Packit how to download it from somewhere else.
Packit for continuous integration
Let's start with a simple example. You need to determine if the new code changes in GitHub or GitLab project built on all stable Fedora distros and CentOS Stream 9 will be successful. The process for such verifications is to get RPM builds for each pull request in your upstream project. The configuration file should include a build job like this:
- job: copr_build
trigger: pull_request
targets:
- fedora-stable-x86_64
- centos-stream-9-x86_64
Easy, right? So what does this configuration accomplish? Packit takes the code changes for each pull request action, submits a new build in the Copr build system, and reports the results in the pull requests, as shown in Figure 1.

You also have access to the actual Copr repository containing the builds. This access may be beneficial if you set up Packit to react to commits or releases because you can provide your RPM builds via the Copr repository to enable anyone to install them. You can also use Packit to do the builds in your Copr repository by specifying the owner and project name. Figure 2 shows one such repository.
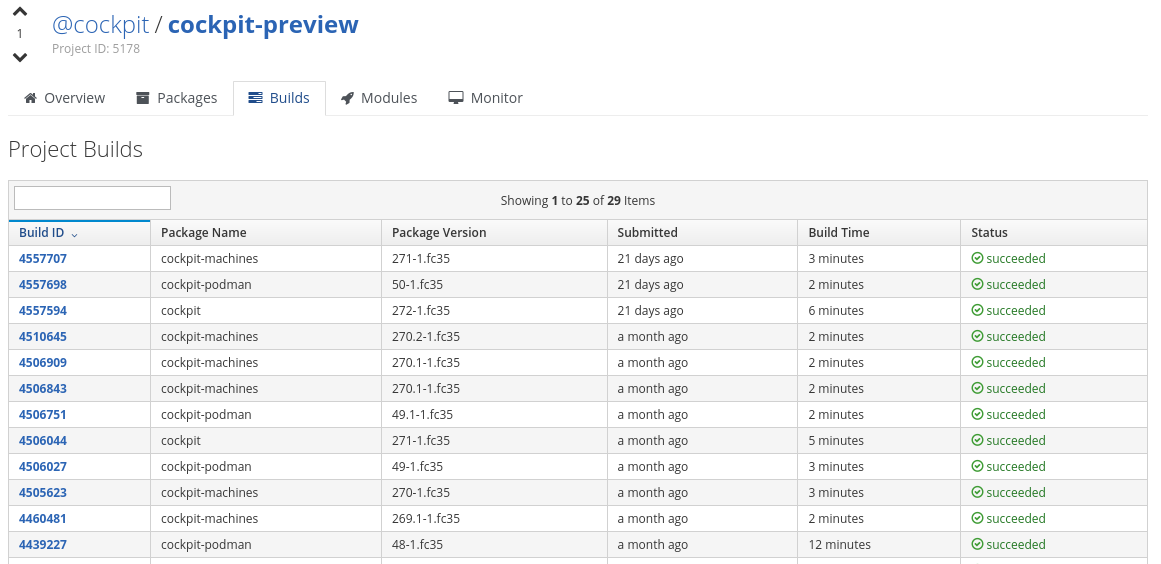
Figure 3 shows a build by Packit in the repository.

Also, if you package your project in Fedora, you will be able to run scratch builds in a similar manner directly in Koji, the Fedora build system.
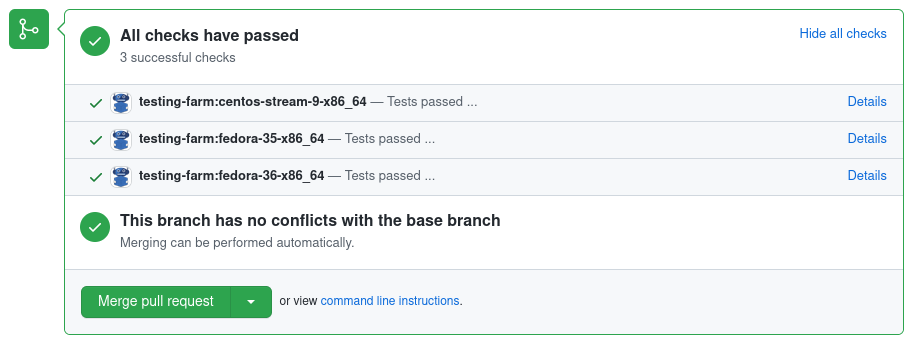
Apart from the RPM builds, you can set up Packit to run your tests in the Testing Farm infrastructure. The tests can either use the built RPMs from Copr or run independently. You can read more information about tests in the Packit documentation. Figure 4 shows how Packit reports test results.
Packit automation for Fedora downstream releases
If you have ever maintained a package in Fedora, you probably know that releasing a new version downstream can be tedious. Packit can help you with boring tasks and do the repetitive work for you. With Packit, you can easily get your upstream releases into Fedora Package Sources, automatically submit builds in the Koji build system, and create Bodhi updates. If you are interested in this kind of automation, make sure to check our release guide.
Ready to give Packit a try?
If you are dealing with any of the situations mentioned, please check our documentation, which will guide you through the Packit setup. If you have any questions, feel free to contact us. We are happy to help and receive feedback or suggestions for features you would like to add.
Last updated: March 15, 2024